Detail Author:
- Name : Cielo Buckridge
- Username : maggie.davis
- Email : tzieme@hotmail.com
- Birthdate : 1998-03-29
- Address : 6435 Boyle Causeway Funkburgh, WI 49866
- Phone : (319) 332-0079
- Company : Bartell-Weber
- Job : Airframe Mechanic
- Bio : Sed ullam nihil est quo. Corrupti recusandae delectus sit explicabo consequuntur. Explicabo modi ut quia debitis ad.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/boganr
- username : boganr
- bio : Ipsa nulla ut vero ut error non. Non ratione quo maiores cumque.
- followers : 177
- following : 32
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/ruth_official
- username : ruth_official
- bio : Qui tempore eum dicta aperiam. Est unde dolores esse minima ut quia et et.
- followers : 142
- following : 449
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@ruth_bogan
- username : ruth_bogan
- bio : Assumenda soluta totam aliquam nesciunt et earum.
- followers : 341
- following : 2602
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/ruth.bogan
- username : ruth.bogan
- bio : Enim voluptatem reiciendis repellat. Ab ut est sed quos quis ratione. Alias voluptatem consequuntur sint.
- followers : 269
- following : 1339
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/ruthbogan
- username : ruthbogan
- bio : Qui quis ducimus saepe sequi deserunt.
- followers : 3043
- following : 1414
When we talk about energy, it's easy to think about the big picture, but sometimes, it's the specific places where these conversations really happen that make all the difference. Pennsylvania, a place with a truly storied past and a natural beauty that stretches from its great lakeshore down to its rolling hills, has, in some respects, become a central point in the bigger discussion about how we get our energy. It's a commonwealth that holds a special spot in American history, and its land, too, has played a pretty significant role in providing resources for a very long time. This is a state that's seen a lot of change, and it continues to adapt as new ways of doing things come along, especially when it comes to tapping into what's beneath the surface.
This particular state, known to many as the "Keystone State," has a distinctive mix of old and new, where historical landmarks stand close to areas that are quite active in today's energy landscape. It’s a place that was one of the very first American colonies, and it still carries that sense of pioneering spirit, even now, as we consider how best to use its abundant natural gifts. We’re going to take a closer look at what makes this state so unique and, in a way, how those qualities shape the ongoing talks about resource extraction, particularly what’s often called "Pennsylvania fracking."
So, what exactly does a state with such a rich background and a truly varied geography mean for something like extracting natural gas from deep within the earth? We’ll be exploring the different aspects of Pennsylvania that are, you know, quite relevant to this topic, from its wide open spaces and its many people to its deep historical roots. It’s really about seeing how the features of this remarkable place play into the bigger picture of energy production and the conversations that come with it.
Table of Contents
- What Makes Pennsylvania So Unique for Fracking Discussions?
- Pennsylvania's Vastness and Its Role in Fracking
- How Does Pennsylvania's History Shape Fracking Conversations?
- Population Density and the Impact of Pennsylvania Fracking
- The Keystone State's Diverse Landscapes and Fracking
- Exploring Pennsylvania's Government and Fracking Policies
- Where Do We Find Pennsylvania Fracking Activities?
- Pennsylvania's Future and Fracking
What Makes Pennsylvania So Unique for Fracking Discussions?
Pennsylvania, as a constituent state of the U.S., holds a rather special spot in the nation's fabric. It was, after all, one of the original thirteen American colonies, a fact that, you know, gives it a certain kind of historical weight. Its boundaries stretch quite a bit, to the north by Lake Erie and New York, and to the east by New York and New Jersey. This geographical placement, too, makes it a significant player in the northeastern part of the country. When we think about Pennsylvania fracking, it's useful to consider the sheer scale of the place. With an area of 119,283 square kilometers, it’s the 33rd largest state by size. That’s a lot of ground, and that vastness, in a way, provides a lot of room for various activities, including those related to energy.
Beyond its physical dimensions, Pennsylvania is also the 5th most populous state in the USA. This combination of being quite large in land area and having a great many people living within its borders creates a unique set of considerations when we talk about resource extraction. The capital city, Philadelphia, which is located on the eastern banks of the Susquehanna River, was the site of truly pivotal moments in American history, like the first and second Continental Congresses. The second one, you know, gave us the Declaration of Independence. So, this is a state with deep roots, a lot of people, and a good deal of land, all of which play into the broader discussion around Pennsylvania fracking.
Pennsylvania's Vastness and Its Role in Fracking
When we think about Pennsylvania, its sheer size is, in a way, one of the first things that comes to mind, especially when considering how land is used. It’s the 33rd largest state in the United States, with a land area that covers 44,817 square miles. That’s a good deal of territory, and this expansive nature means there are many different types of environments within its borders. From the shores of Lake Erie in the north to the Appalachian Mountains that run through it, the landscape is incredibly varied. This extensive land area, arguably, offers a lot of space for various kinds of development, including industrial activities like those associated with Pennsylvania fracking.
The presence of Mount Davis, the state's highest point at 3,213 feet above sea level, also tells us something about the diverse terrain. This kind of geographical variation means that discussions about land use, and specifically about where and how resource extraction might happen, are quite complex. The size of the state means that there are both heavily populated areas and stretches of more rural, open land. This mix, you know, often leads to different perspectives and concerns about how large-scale industrial operations, like those involved in Pennsylvania fracking, might interact with the environment and the people who live there. It’s a bit like a big puzzle with many different pieces that need to fit together.
How Does Pennsylvania's History Shape Fracking Conversations?
Pennsylvania, often called the "Keystone State," has a truly captivating blend of rich history, diverse culture, and stunning landscapes. This historical depth is, in some respects, a major part of its identity. It was, for example, one of the 13 original colonies, and this fact alone means it has seen centuries of development and change. The capital, Philadelphia, was the very spot where the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence were created. These historical milestones mean that the state has a long tradition of public discourse and, you know, of grappling with important decisions that affect its people and its future.
This historical context, quite frankly, plays a role in how contemporary issues, like those surrounding Pennsylvania fracking, are discussed. The state has always been a place where big ideas are debated and where the rights and well-being of its citizens are considered. This tradition of civic engagement means that when new industries or new ways of using land and resources come along, there's often a strong public voice. The legacy of independence and liberty, which is even part of the state motto – "Virtue, Liberty, and Independence" – suggests a populace that values its freedoms and, too, its ability to shape its own destiny. This deep historical backdrop provides a framework for how people approach and talk about modern resource development.
Population Density and the Impact of Pennsylvania Fracking
As we’ve noted, Pennsylvania is the 5th most populous state in the United States. This means a great many people call this place home, from the bustling areas around Philadelphia and Pittsburgh to the more spread-out communities in the central and western parts of the state. The fact that so many people live here, you know, creates a very different dynamic when we talk about industrial activities like Pennsylvania fracking. When there are more people in an area, there are naturally more concerns about how such activities might affect daily life, local infrastructure, and the general well-being of residents.
The distribution of this population is also something to consider. While there are large urban centers, there are also numerous smaller towns and rural communities that might be closer to areas where resource extraction takes place. This close proximity, arguably, brings the discussions around Pennsylvania fracking right into people's backyards, so to speak. It means that conversations about things like land use, water resources, and air quality become very personal for a lot of people. The sheer number of residents means that any decisions made about large-scale industrial operations will affect a significant portion of the country's population, making these discussions particularly important and, well, quite sensitive for many.
The Keystone State's Diverse Landscapes and Fracking
Pennsylvania, known as the "Keystone State," truly boasts a captivating blend of stunning landscapes. From the serene shores of Lake Erie in the north to the rugged peaks of Mount Davis and the gentle curves of the Susquehanna River, the state offers an incredible variety of natural settings. This diversity is, in a way, a defining characteristic of the land itself. It means that any large-scale activity that uses the land, like Pennsylvania fracking, has to contend with a wide array of environmental considerations.
Think about it: you have forested mountains, agricultural plains, and river valleys, all within the same state. Each of these different types of environments has its own unique features and, too, its own sensitivities. For example, what works in one geological area might be very different from what's needed in another. This varied topography and natural beauty mean that discussions about where and how to conduct resource extraction are often very detailed and specific to local conditions. It’s not just one type of land; it’s a whole spectrum, and that, you know, makes the planning and execution of projects like Pennsylvania fracking a bit more involved, requiring careful thought about the particular surroundings.
Exploring Pennsylvania's Government and Fracking Policies
As the home base of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the state government plays a very important role in overseeing various activities within its borders. We can explore the services and resources offered by this government, which includes, naturally, how it manages its natural resources and regulates industrial operations. The state has official symbols, flags, maps, and even its own constitution, all of which point to a well-established system of governance. This framework, arguably, is what guides how discussions and decisions about something like Pennsylvania fracking are made.
The government is responsible for creating and upholding the rules that govern land use, environmental protection, and public safety. This means that when it comes to resource extraction, there are specific guidelines and processes that must be followed. Understanding these governmental structures and the policies they put in place is, you know, pretty essential for anyone looking to grasp the full picture of how Pennsylvania approaches the topic of fracking. It’s about how the collective will of the people, expressed through their representatives, shapes the industrial landscape and ensures, in some respects, a balance between development and preservation.
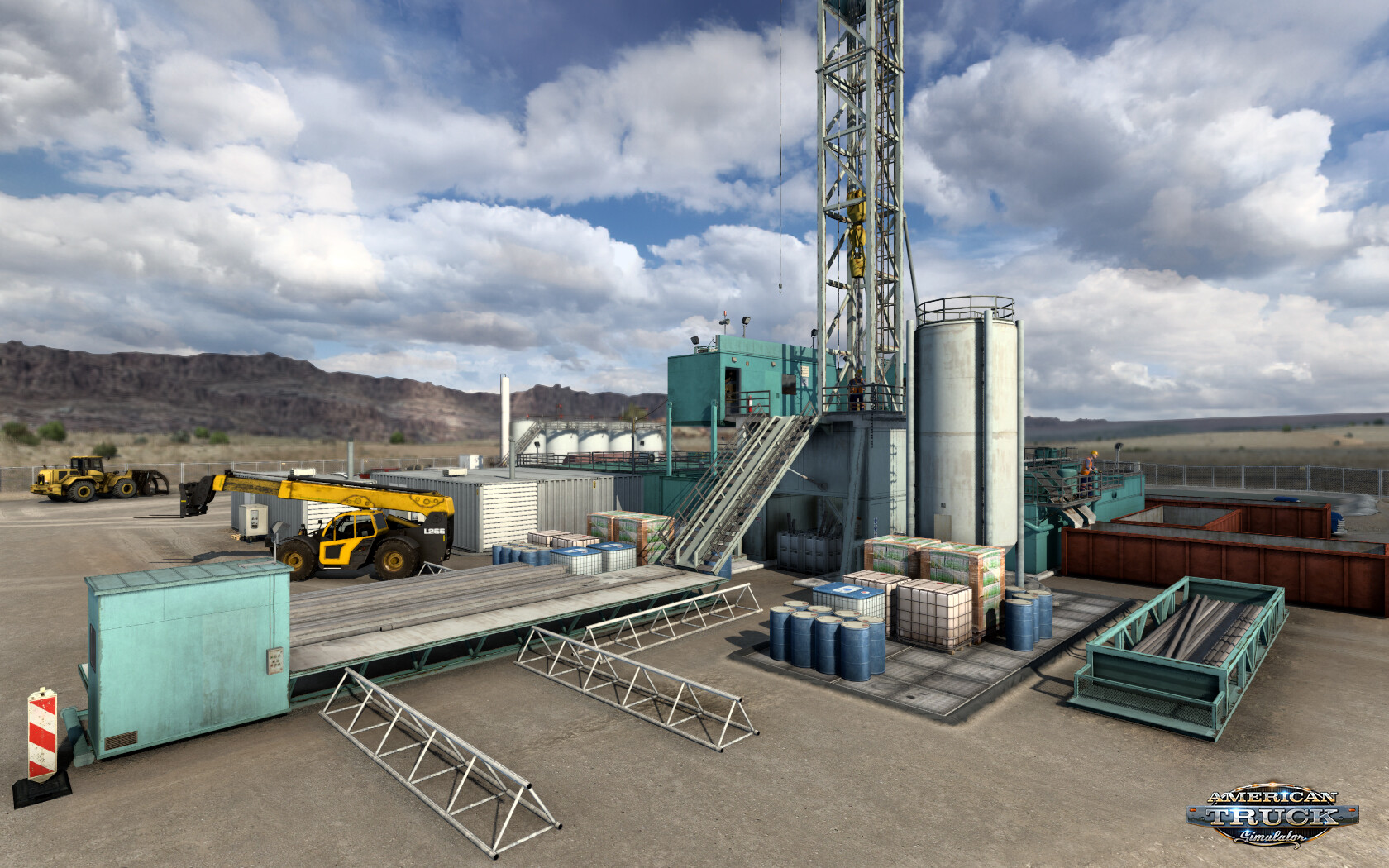
Where Do We Find Pennsylvania Fracking Activities?
Given Pennsylvania’s large land area and its diverse geological makeup, it's perhaps no surprise that discussions about resource extraction are often tied to specific regions. While the provided text doesn't pinpoint exact locations for fracking, it does tell us about the state's overall geography. We know it’s bounded by Lake Erie and New York to the north, and New York and New Jersey to the east. The Susquehanna River, too, plays a notable role, with the capital city of Philadelphia situated on its eastern banks. This kind of geographical information helps us, you know, visualize the broad areas of the state.
Knowing that Pennsylvania has varied landscapes, from mountains like Mount Davis to wide plains and river systems, suggests that the potential for resource extraction might be found in different geological formations across the state. While we can't specify exact sites for Pennsylvania fracking without adding new context, we can infer that the activity would typically be concentrated in areas where the underlying geology is suitable for natural gas deposits. This often means regions that might be less densely populated or have specific types of rock formations. It’s really about connecting the dots between the state’s natural features and where certain industrial operations might realistically occur.
Pennsylvania's Future and Fracking
As a state with a truly rich heritage and a forward-looking spirit, Pennsylvania is always, you know, thinking about its future. The information resource links to the state homepage, symbols, flags, maps, constitutions, representatives, songs, birds, flowers, and trees all point to a deeply rooted identity and a commitment to its unique character. This forward-looking perspective naturally extends to how the state manages its resources and how it balances economic development with environmental stewardship. The ongoing conversations around Pennsylvania fracking are, in a way, a part of this larger discussion about the state’s path forward.
The decisions made today about resource extraction will, arguably, have a lasting impact on the state’s landscapes, its communities, and its economy. It's about finding ways to utilize natural gifts while also preserving the qualities that make Pennsylvania such a special place, like its captivating blend of history and stunning natural beauty. The dialogue about Pennsylvania fracking is, therefore, not just about energy; it’s about the kind of future the "Keystone State" wants to build for its residents and for generations to come. It’s a pretty big topic, really, with a lot of different angles to consider.
This article has explored Pennsylvania’s unique characteristics—its extensive land area, its significant population, its deep historical roots, and its varied landscapes—and how these attributes shape the broader discussions around resource extraction, particularly in the context of Pennsylvania fracking. We’ve looked at how the state’s size provides space for industrial activities, how its rich history influences public discourse, and how its population density brings specific concerns to the forefront. The article also touched upon the role of the state government in policy-making and considered how Pennsylvania’s diverse geography might relate to where such activities occur. Finally, it considered the ongoing dialogue about fracking as part of the state’s larger vision for its future.